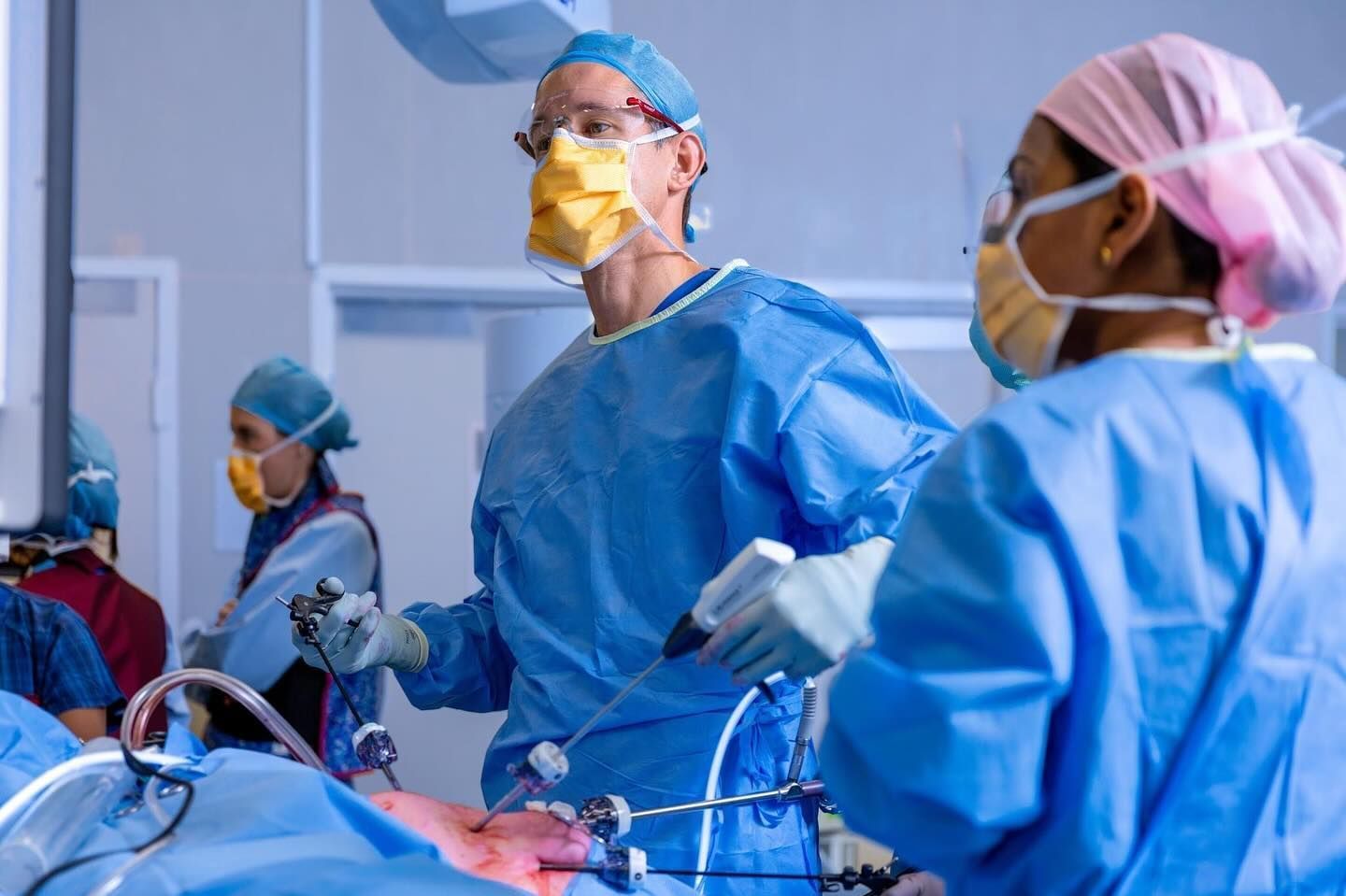
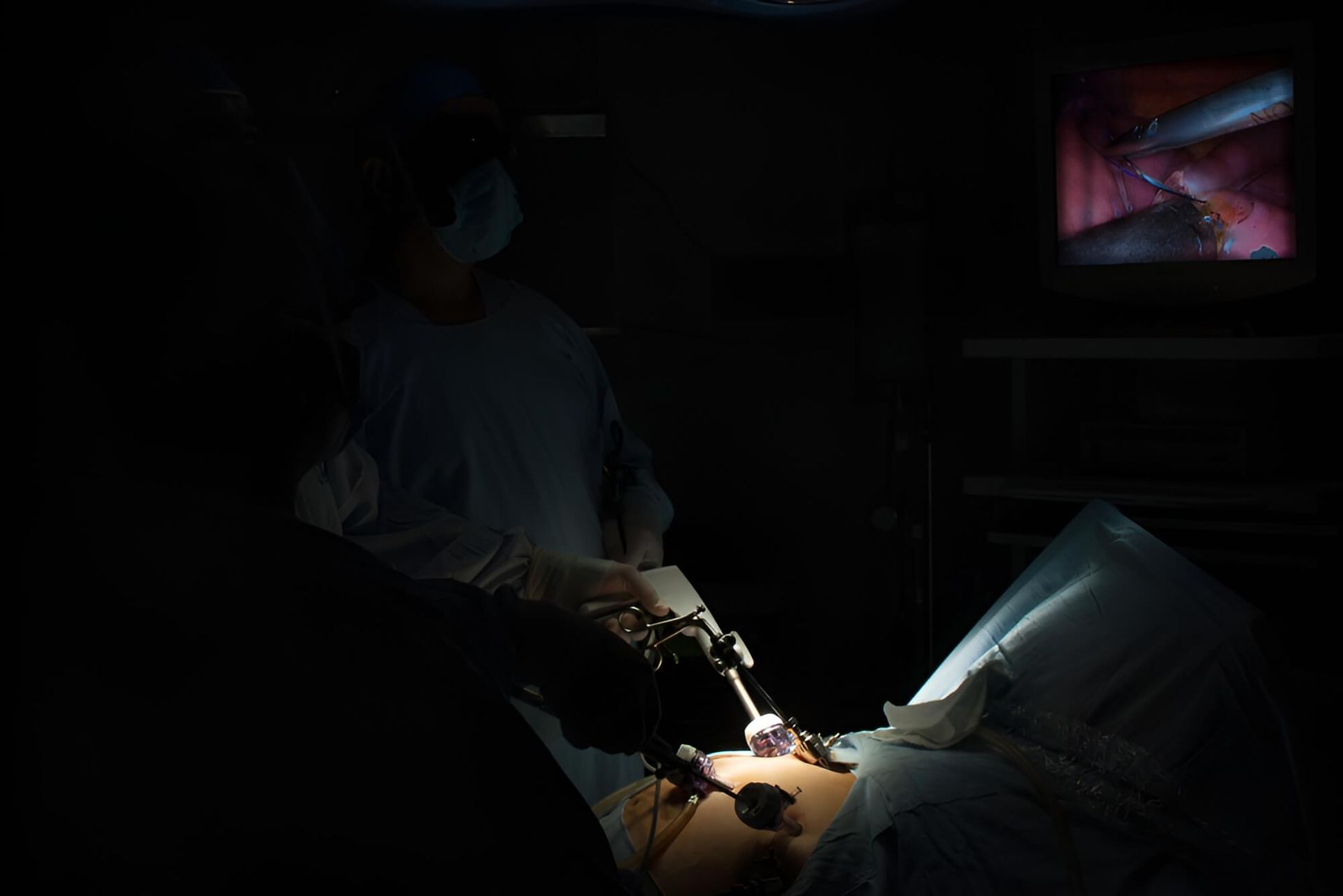
We Offer Laparoscopic Cardiomyotomy in Brisbane
Wide Range of Surgical Treatments
Support for Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS)
Non-Judgemental Practitioners
What Is Laparoscopic Cardiomyotomy?
Laparoscopic cardiomyotomy, or Achalasia, refers to keyhole surgery to divide the lower oesophageal sphincter muscle, usually performed for achalasia. A gentle fundoplication is performed to reduce the risk of reflux. The procedure requires a 1 – 2 night stay in hospital. Local anaesthetic in the incisions and abdominal cavity means that pain is minimal.
Depending on the type of achalasia you have, swallowing will usually be significantly improved by surgery.
Conversion to open surgery is extremely rare (less than 0.5%).
Indications & Side Effects
Indications
Achalasia and other oesophageal motility disorders cause dysfunction of the swallowing process, resulting in dysphagia (swallowing difficulty) and chest pain (from abnormal spasm of the oesophageal muscle).
Surgery is indicated if symptoms are severe. The greatest benefit is obtained for patients with a tight lower oesophageal sphincter who have some residual oesophageal body function (ability to contract).
Side effects
Side effects of surgery, other than mild pain, are very rare. Some patients experience reflux afterwards, though this can usually be controlled well with medication. Cardiomyotomy is not a cure for achalasia. The disease usually progresses to cause recurrent symptoms some years later. Many patients will ultimately need their oesophagus removed (oesophagectomy).